Modeling and density estimation of Heterodera schachtii populations




Decision making by crop rotation designs
Formerly a Java applet for online applications have been placed at this position. The security demands of Java or browsers of today are so strict, the applet does not even run on my own computer anymore. Alternatively, we produced the results graphically for all combinations available and provide the basic backgrounds.
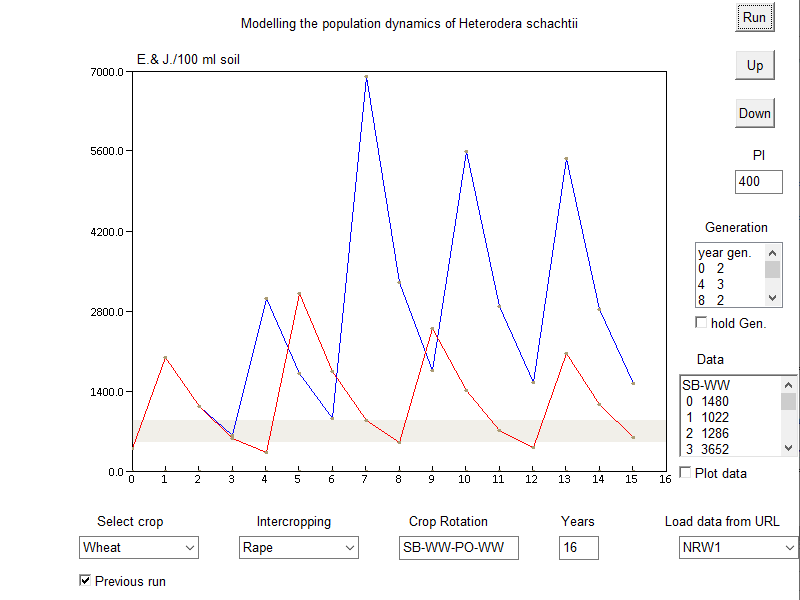
The model predicts the long term dynamics of BCN Heterodera schachtii on a discrete year axis. An initial value of the population Pi (or an estimator of that value) is required. The numbers of generations per sugar beet season determine the population growth (usually 2 or 3, see table 1) with (susceptible) sugar beet varieties, the chosen non-hosts as part of the crop rotation reduce the population with crop specific rates. Both processes result in crop rotation specific population densities. The objectives are to keep the population density of BCN below the threshold level of 500 E&J/100 ml soil at planting sugar beet. The threshold value must not be seen that strict anymore, depending how much risk you take, up to ~800-900 E&J/100 ml soil might be tolerable (gray area in fig. 1).
| Table 1 | |
|---|---|
| Generation | Climate |
| 1 | cold |
| 2 | standard |
| 3 | warm |
| 4 | very warm |
| 5 | nowadays possible ? |
Small insertion:
The overall population range or theoretical model
boundaries generated by the choice of generations and size of crop rotation
are shown under the following Link
The following abbreviations of parameterised crops are used:
SB: sugar beet; WW: winter wheat; WB: winter barley; RA: rape; BE: beans; OAT: oat; RYE: rye; MA: maize; PO: potato; SG: summer barley; SW: summer wheat;
The following intercropping species are implemented: (RA): rape;
(MU); mustard; (OIL): oil radish; PH: Phacelia; mustard and oil raddish as resistant varieties, rape in short time culture (ca. for 6 weeks).
Procedure
Step 1: Create a crop rotation from the parameterised crops available.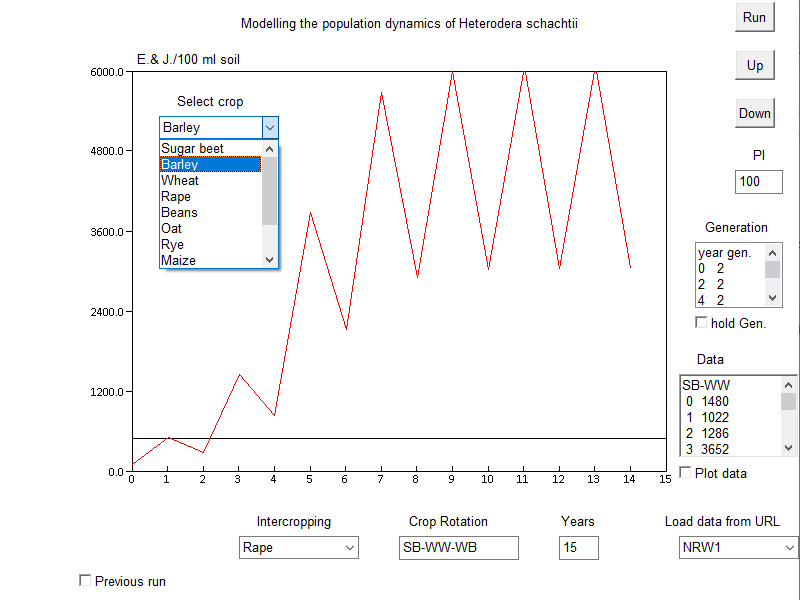
Choose the crops from the menue to create a reasonable crop rotation
Step 2: Choose an intercropping procedure (kind and/or position within the rotation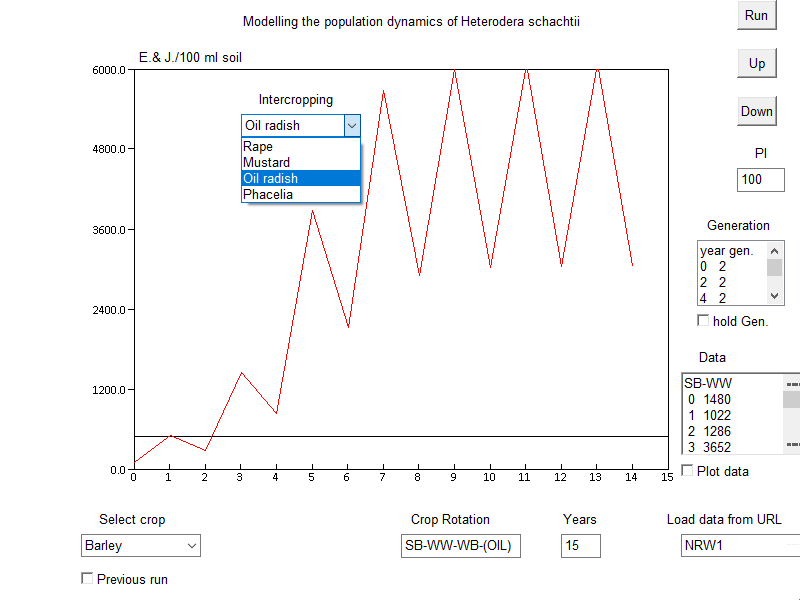

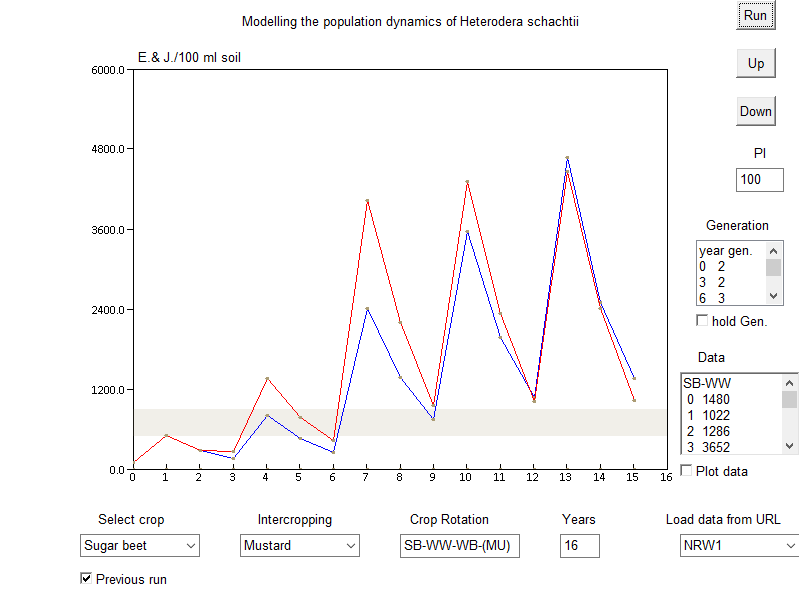
The use of resistant intercrops might have a negative effect if the initial population is (far?) below threshold level. The population increases compared to crop rotations without catchcrops (red line), the critical density range is exceeded in year 9. It takes another two rotations (year 15) to get a significant lower population than the standard rotation again.
 Evaluation reinvented
Evaluation reinvented